- Call us!
- +86 531 8887 6213
- cathy@winner-psa.com
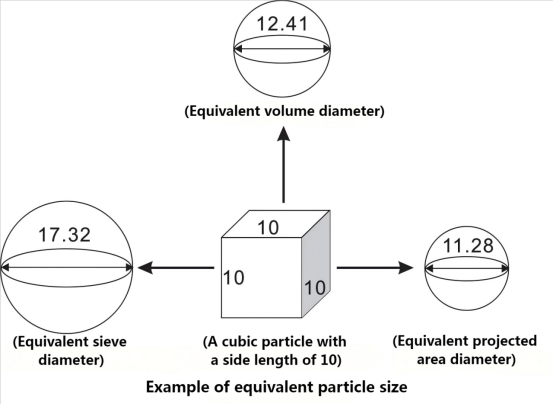
Most actual particles are irregular in shape and not standard spheres. Most actual particles are irregular in shape and not standard spheres. The concept of equivalent particle size is introduced to simplify the description of their size: when a physical property of a particle (such as volume, weight, sedimentation velocity, etc.) is the same or similar to that of a homogeneous spherical particle, the diameter of the spherical particle is used to represent the particle's diameter.
The equivalent particle size can be divided into the following categories:
1. Screening Particle Size: The smallest square-hole sieve aperture that a particle can pass through. This is the most intuitive and commonly used equivalent particle size, representing the minimum cross-sectional width of a particle and widely used in industrial screening processes and controls.
2. Equivalent volume diameter: The diameter of a homogeneous spherical particle with the same volume as the particle being measured. The particle size measured by the laser method is the equivalent volume diameter.
3. Equivalent Sedimentation Diameter: The diameter of a sphere of equal density at the same sedimentation velocity in the same fluid. The particle size measured by sedimentation is the equivalent sedimentation diameter, also known as the Stokes diameter.
4. Equivalent resistance diameter: The diameter of a homogeneous spherical particle with the same resistance as the particle being measured. The particle size measured by the Coulter method is the equivalent resistance diameter.
5. Equivalent Projected Area Diameter: The diameter of a spherical particle with the same projected area as the particle being measured. The equivalent projected area diameter is measured by the microscopic imaging method.
The equivalent particle size is not the only, absolute size for a particle! Its value depends entirely on the physical principle underlying the measurement. Different methods use different equivalent conditions, and the results vary, but they are all valid ways to describe particle size under specific conditions.
Copyright © Jinan Winner Particle Instrument Stock Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved | Sitemap
Keywords:
Laser Particle Size Analyzer Spray Particle Size Analyzer Particle Image System Online Particle Size Analyzer Particle Size Analyzer particle size distribution particle size analyzer manufacturer Laser diffraction particle size analyzer particle size malvern particle size analyzer